A dynamic peripheral immune landscape during human pregnancy
FAYETTEVILLE, GA, UNITED STATES, April 16, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- This study uncovers dynamic immune adaptations during pregnancy through single-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral blood mononuclear cells at different pregnancy stages. A gradual reduction in cytotoxicity of T and NK cells, along with decreased MHC-II and CD40 signaling in T and B cells, suggests weakened adaptive immunity. Meanwhile, upregulated pro-inflammatory genes in monocytes may compensate for this reduction. Late pregnancy shows a transition toward immune activation in dendritic and CD4+ T cells. Notably, we highlight a novel pro-aging effect of pregnancy, which may reverse postpartum. These findings enhance our understanding of pregnancy immunity and its impact on disease risk.
Pregnancy triggers profound immune adaptations to ensure fetal tolerance and successful delivery; however, these changes can alter maternal susceptibility to various diseases. Traditional models of maternal immunity have overlooked the dynamic immune shifts across different pregnancy stages and their implications for maternal health. During pregnancy, the maternal immune system undergoes widespread adaptive changes to ensure fetal tolerance and facilitate normal delivery. This unique immune state affects the mother's susceptibility to diseases, manifesting differently in the early, middle, and late stages of pregnancy.
Research indicates that while the risk of infections increases during pregnancy, the incidence of autoimmune diseases, such as uveitis, decreases, only to rise again postpartum. Therefore, exploring immune system differences across the various stages of pregnancy is needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of pregnancy-related immune disorders.
In a study led by Prof. Wenru Su and Prof. Xianggui Wang, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed on peripheral blood immune cells from pregnant women at various stages of pregnancy, postpartum, and healthy controls.
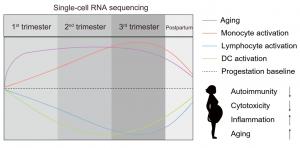
“We established a high-resolution immune map of maternal immune changes, uncovering key insights into pregnancy-associated immune adaptations and immune aging,” explains Su. “Pregnancy induces a notable decline in adaptive immunity, particularly in T and B cells, while activating monocytes as a compensatory mechanism.
The researchers also observed a transition from immune suppression to activation in late pregnancy, potentially contributing to labor and delivery. Overall, the team’s findings, published in KeAi’s Fundamental Research, highlight three key discoveries:
Suppressed Adaptive Immunity: Pregnancy reduces cytotoxic gene expression in CD8+ T and NK cells, particularly in late pregnancy, and downregulates Th17 cell differentiation and B-cell signaling, resulting in a weakened adaptive immune response.
Compensatory Inflammatory Response: Monocytes exhibit increased activation and pro-inflammatory gene expression, particularly through IL-1 signaling, which may compensate for the decline in adaptive immunity and align with physiological inflammation in late pregnancy.
Immune Aging During Pregnancy: Pregnancy promotes immune aging, as evidenced by increased oxidative stress, inflammation, and expression of senescence markers such as CDKN1A and STAT3 in monocytes and NK cells. Notably, these changes are partially reversed postpartum, suggesting that antioxidant therapies may aid postpartum recovery.
“Our study provides the first single-cell resolution of maternal immune dynamics during pregnancy,” adds Su. “The increased monocyte activity in late pregnancy could serve as a potential predictor of birth outcomes, and the reversal of immune aging postpartum highlights the need for antioxidant interventions to support maternal recovery.”
References
DOI
10.1016/j.fmre.2022.06.011
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fmre.2022.06.011
Funding Information
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Excellent Young Scientists Fund (82122016) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0105804).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
leagend T31 Sets New Standard for Affordable and Accurate OBD II Diagnostics
Couple Opens Unique '432Hz' Live Music Sanctuary on Spain's Costa del Sol for Summer Vibes and Son Awareness
انتشار خيمۀ حسب حال راز آميز عمر خيام: بازدوزى منطقى و ترجمۀ منظوم هزار رباعى ميكدۀ سعادتش بر اساس روش هستى شناسى خود او
Kalendarium
Więcej ważnych informacji
 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

Handel

Ze względu na różnice w cenach surowce wtórne przegrywają z pierwotnymi. To powoduje problemy branży recyklingowej
Rozporządzenie PPWR stawia ambitne cele w zakresie wykorzystania recyklatów w poszczególnych rodzajach opakowań. To będzie oznaczało wzrost popytu na materiały wtórne pochodzące z recyklingu. Obecnie problemy branży recyklingu mogą spowodować, że popyt będzie zaspokajany głównie przez import. Dziś do dobrowolnego wykorzystania recyklatów nie zachęcają przede wszystkim ceny – surowiec pierwotny można kupić taniej niż ten z recyklingu.
Przemysł spożywczy
Rośnie presja konkurencyjna na unijne rolnictwo. Bez rekompensat sytuacja rolników może się pogarszać

Rolnictwo i żywność, w tym rybołówstwo, są sektorami strategicznymi dla UE. System rolno-spożywczy, oparty na jednolitym rynku europejskim, wytwarza ponad 900 mld euro wartości dodanej. Jego konkurencyjność stoi jednak przed wieloma wyzwaniami – to przede wszystkim eksport z Ukrainy i niedługo także z krajów Mercosur, a także presja związana z oczekiwaniami konsumentów i Zielonym Ładem. Bez rekompensat rolnikom może być trudno tym wyzwaniom sprostać.
Transport
Infrastruktury ładowania elektryków przybywa w szybkim tempie. Inwestorzy jednak napotykają szereg barier

Liczba punktów ładowania samochodów elektrycznych wynosi dziś ok. 10 tys., a tempo wzrostu wynosi ok. 50 proc. r/r. Dynamika ta przez wiele miesięcy była wyższa niż wyniki samego rynku samochodów elektrycznych, na które w poprzednim roku wpływało zawieszenie rządowych dopłat do zakupu elektryka. Pierwszy kwartał br. zamknął się 22-proc. wzrostem liczby rejestracji w ujęciu rocznym, ale kwiecień przyniósł już wyraźne odbicie – o 100 proc.
Partner serwisu
Szkolenia

Akademia Newserii
Akademia Newserii to projekt, w ramach którego najlepsi polscy dziennikarze biznesowi, giełdowi oraz lifestylowi, a także szkoleniowcy z wieloletnim doświadczeniem dzielą się swoją wiedzą nt. pracy z mediami.








.gif)

 |
| |
| |
|