Ultrafast neuromorphic computing driven by polariton nonlinearities
GA, UNITED STATES, June 6, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Neuromorphic computing, inspired by the human brain, offers a path to faster and more efficient AI. In a pioneering breakthrough, Chinese scientists demonstrate the first use of perovskite microcavity exciton-polariton as a platform for neuromorphic computing, achieving 92% accuracy in digit recognition with single-step training. Operating at room temperature and driven by strong optical nonlinearity, the system enables ultrafast and power-efficient computation—paving the way for next-generation light-based intelligent hardware.
Neuromorphic computing, inspired by the human brain, is considered as the next-generation paradigm for artificial intelligence (AI), offering dramatically increased speed and lower energy consumption. While software-based artificial neural networks (ANNs) have made remarkable strides, unlocking their full potential calls for physical platforms that combine ultrafast operation, high computational density, energy efficiency, and scalability. Among various physical systems, microcavity exciton polaritons have attracted attention for neuromorphic computing due to their ultrafast dynamics, strong nonlinearities, and light-based architecture, which naturally align with the requirements of brain-inspired computation. However, their practical use has been hampered by the need for cryogenic operation and intricate fabrication processes.
In a new paper published in eLight, a team of scientists led by Professor Qihua Xiong from Tsinghua University and Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences report a demonstration of neuromorphic computing utilizing perovskite microcavity exciton polaritons operating at room temperature. Their novel system achieves high-speed digit recognition with 92% accuracy using only single-step training and opens new opportunities for scalable, light-driven neural hardware.
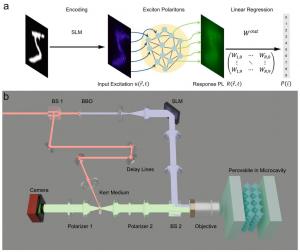
The core of their system is a planar FAPbBr3 perovskite microcavity which supports exciton-polariton condensation under non-resonant optical pumping. Input images from the MNIST dataset are optically encoded by a spatial light modulator (SLM) and projected onto the microcavity as spatially structured excitation beams. The resulting polariton emission patterns serve as the output of the ANN, which is then linearly processed using ridge regression. Remarkably, this scheme requires no predefined network structure—only the physical response of the polariton system—and achieves competitive accuracy using a lightweight training set of 900 images.
“Unlike conventional approaches that rely on prefabricated structures or predefined network nodes, our method employs a fully connected spatial mapping, utilizing the entire perovskite sample area without additional structural constraints,” the corresponding author Qihua Xiong replied. This not only improves the system's scalability but also simplifies experimental realization.
What makes this system stand out is the intrinsic nonlinear and dynamical response of the polaritons. The researchers show that below the condensation threshold, the system behaves nearly linearly, while near and above threshold, nonlinearities emerge sharply, enhancing pattern discrimination. Moreover, by applying ultrafast Kerr-gated time-resolved photoluminescence, the team probes the temporal evolution of polariton responses. They find that polariton dynamics unfold on the picosecond scale and exhibit time-dependent nonlinear mappings, which significantly broaden the system’s capacity for processing complex and temporally varying inputs.
The researchers conclude that “perovskite microcavity exciton polaritons offer ultrafast processing speeds on the picosecond timescale and exhibit exceptionally strong nonlinear interactions, significantly surpassing those in traditional photonic systems.” These attributes make them powerful candidates for future physical neural networks capable of real-time, energy-efficient AI.
This work highlights the growing role of halide perovskites in next-generation photonic computing and marks an important step toward developing all-optical neuromorphic hardware—free from the energy and speed limitations of traditional electronics.
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43593-025-00087-9
Funding information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 12434011) and the State Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Physics at Tsinghua University.
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Global HVAC Maintenance Services Market Set for Steady Growth Through 2034
Global Product Design Development Services Market to Double by 2034 Driven by AI, Sustainability, and Digital Innovation
Property Tax Service Market to Reach USD 12 Billion by 2034, Driven by Urbanization and Digital Transformation
Więcej ważnych informacji
 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

Konsument

Wzrost sprzedaży piw bezalkoholowych idzie w parze z inwestycjami w zieloną energię. Kompania Piwowarska ogranicza ślad węglowy i wspiera lokalne inicjatywy
Kompania Piwowarska kontynuuję realizację strategii „Lepsza Przyszłość 2030”, w której łączy ambitne cele środowiskowe, edukacja konsumentów oraz rozwój segmentu piw bezalkoholowych z realnym wsparciem dla lokalnych społeczności. Firma, będąca liderem polskiego rynku piwa, ogranicza emisję CO₂, zwiększa udział opakowań zwrotnych i angażuje pracowników w wolontariat, w tym m.in. w pomoc dla ofiar powodzi na Dolnym Śląsku.
Handel
D. Joński: Europa musi chronić swój rynek poprzez cła i wysokie standardy bezpieczeństwa dla importowanych towarów. Powinniśmy budować własny przemysł oparty na tańszej energii

Tańsza energia, a przez to niższe koszty produkcji w Europie to jeden z kierunków, który wskazuje Unia Europejska w rywalizacji z tanimi towarami z Azji, głównie z Chin. Jednocześnie rynek Starego Kontynentu powinien być chroniony poprzez zbalansowane cła oraz wysokie standardy bezpieczeństwa stawiane importowanym produktom. Zdaniem europosła Dariusza Jońskiego ważne jest rozwijanie przemysłu w Europie bez względu na narodowość właścicieli. Relacje z Chinami muszą zostać na nowo zdefiniowane i przebiegać na równych zasadach.
Handel
Poprawia się jakość raportów dużych spółek giełdowych dotyczących zrównoważonego rozwoju. Pozostają też obszary do dopracowania

Ekspertki i eksperci z Deloitte’a przeprowadzili analizę ujawnień taksonomicznych spółek notowanych na Giełdzie Papierów Wartościowych, która objęła sprawozdania z działalności za rok 2024 w części dotyczącej zrównoważonego rozwoju. To trzeci rok ujawniania stopnia zgodności przedsiębiorstw z Taksonomią Unii Europejskiej, co przekłada się na zwiększoną jakość i porównywalność prezentowanych danych. Jednocześnie można oczekiwać, że inwestycje zgodne z Taksonomią będą coraz istotniejszym elementem strategii rozwoju przedsiębiorstw w kolejnych latach.
Partner serwisu
Szkolenia

Akademia Newserii
Akademia Newserii to projekt, w ramach którego najlepsi polscy dziennikarze biznesowi, giełdowi oraz lifestylowi, a także szkoleniowcy z wieloletnim doświadczeniem dzielą się swoją wiedzą nt. pracy z mediami.








.gif)

 |
| |
| |
|