RNA-Binding Proteins and Circular RNAs: A New Frontier in Cancer Therapy
SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, May 12, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ --
The interaction between RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs) has emerged as a key area of interest in understanding cancer biology. As critical regulators of gene expression, RBPs control the formation and function of circRNAs, influencing various cancer-related processes such as tumor proliferation, metastasis, drug resistance, and immune evasion. This dynamic interplay has positioned the circRNA-RBP network as a promising target for developing innovative cancer therapies.
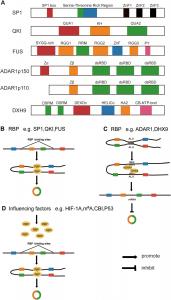
CircRNAs are unique RNA molecules formed through a back-splicing mechanism that connects the 5' and 3' ends of precursor mRNA. Previously considered splicing errors, circRNAs are now recognized for their roles as molecular sponges for microRNAs (miRNAs) and proteins, as well as their capacity to regulate RNA-protein interactions. RBPs play a crucial role in circRNA biogenesis and function, with specific proteins like QKI, SP1, FUS, ADAR1, and DHX9 shown to either promote or inhibit circRNA production, thereby shaping tumor characteristics.
RBPs such as QKI and FUS enhance circRNA formation by facilitating the reverse splicing process. For instance, QKI’s binding to precursor mRNA promotes circularization, while FUS interacts with circRNAs to form positive feedback loops, sustaining the expression of oncogenic circRNAs. In contrast, ADAR1 and DHX9 suppress circRNA production by editing RNA sequences or destabilizing RNA structures. The intricate regulation by RBPs makes circRNAs pivotal in controlling tumor growth, metastasis, and response to therapy.
A notable aspect of circRNA-RBP interactions is their role in the tumor microenvironment (TME), where factors like hypoxia alter RBP expression and activity. Hypoxia-induced changes can either enhance or inhibit circRNA formation, affecting tumor behavior. Furthermore, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification on circRNAs has been shown to modulate their interaction with RBPs, impacting tumorigenesis and cancer progression. This modification not only affects RBP binding but also regulates circRNA stability and translation, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target.
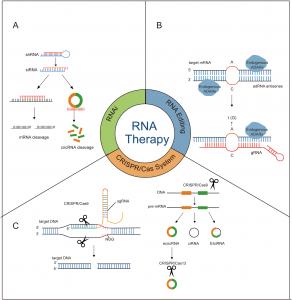
The discovery of the circRNA-RBP network has spurred the development of RNA-based therapies. Techniques such as RNA interference (RNAi), RNA editing, and the CRISPR/Cas system are being explored to target specific RBPs and circRNAs. By disrupting harmful circRNA-RBP interactions or enhancing beneficial ones, these therapies aim to inhibit cancer progression while minimizing off-target effects. Innovations like ADAR-mediated RNA editing and CRISPR-Cas13 systems demonstrate the feasibility of precisely targeting the circRNA-RBP axis, paving the way for personalized cancer treatment.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Lixia Li, Chunhui Wei, Yu Xie, Yanyu Su, Caixia Liu, Guiqiang Qiu, Weiliang Liu, Yanmei Liang, Xuanna Zhao, Dan Huang, Dong Wu, Expanded insights into the mechanisms of RNA-binding protein regulation of circRNA generation and function in cancer biology and therapy, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 4, 2025, 101383, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101383
Funding Information:
National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China 2022A1515011731
National Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China 2021A1515011062
Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (China) 20221211
Project of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong, China 2020A01016
Project of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong, China 2020B01346
Project of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong, China 2021A05077
Project of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong, China 2016B01062
Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (China) 4SG21231G
Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (China) LCYJ2017A003
Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (China) CLP202113001
Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (China) CLP2021B001
Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (China) LCYJ2020B008
Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (China) BK201616
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
editor|genesndiseases.com| |editor|genesndiseases.com
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Bipolar Disorder Therapeutics Market to Reach USD 10,970M by 2035 | Fact.MR Report
ELECFREAKS Introduces micro:bit Jacdac Smart Exploration Kit, Simplifying Smart Device Creation
After Synapse Collapse and Evolve Bank Action, U.S. Banks Confront a Reckoning in BaaS
Kalendarium
Więcej ważnych informacji
 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

Finanse

Uchodźcy z Ukrainy pomogli wygenerować 2,7 proc. PKB Polski w 2024 roku. Napływ nowych pracowników znacznie zmienił polski rynek pracy
Uchodźcy z Ukrainy coraz lepiej radzą sobie na polskim rynku pracy – pracuje 69 proc. z nich – wynika z najnowszego badania przeprowadzonego przez Deloitte dla UNHCR. Jednocześnie wciąż w tym obszarze jest wiele wyzwań, w tym bariery językowe czy kwestie dotyczące uznawania kwalifikacji, np. w zawodach medycznych i prawniczych. Na rosnącej aktywności zawodowej Ukraińców mocno skorzystała polska gospodarka, ale też sam rynek pracy: wzrosła konkurencja, a Polacy uzyskali możliwość specjalizacji i objęcia stanowisk menedżerskich, eksperckich i technicznych.
Ochrona środowiska
W UE wciąż więcej kontroli działań firm w ramach ESG niż zachęt. Konieczne jest złagodzenie podejścia

Instytucje unijne powinny bardziej koncentrować się na celach i możliwościach rozwoju, jakie daje ESG, a nie kontroli działań firm w tym obszarze i obowiązków sprawozdawczych – twierdzą przedstawiciele organizacji Business for Good. Konieczne jest więc złagodzenie obowiązujących regulacji. Europa powinna również dążyć do utworzenia wspólnego rynku o ujednoliconych przepisach i mechanizmach.
Konsument
Wakacje wyzwaniem dla operatorów komórkowych. W najpopularniejszych kurortach ruch w sieci rośnie nawet pięciokrotnie

Długie weekendy i wakacje to wymagający czas dla operatorów komórkowych. W najbardziej obleganych kurortach udział abonentów tylko sieci Play w stosunku do liczby mieszkańców przekracza 500 proc. Dlatego operator planuje dalszą rozbudowę swojej sieci komórkowej do minimum ponad 15 tys. stacji bazowych. W latach 2020–2024 Play zainwestował w sieć i częstotliwość ponad 6 mld zł.
Partner serwisu
Szkolenia

Akademia Newserii
Akademia Newserii to projekt, w ramach którego najlepsi polscy dziennikarze biznesowi, giełdowi oraz lifestylowi, a także szkoleniowcy z wieloletnim doświadczeniem dzielą się swoją wiedzą nt. pracy z mediami.







.gif)

 |
| |
| |
|