Soil microbes: the unsung heroes of agriculture in the face of salinity
FAYETTEVILLE, GA, UNITED STATES, July 1, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Salinity is a rising threat to global agriculture, severely limiting crop productivity and damaging soil health. New research reveals how the microscopic world beneath our feet might be the key to solving this issue. Soil microbiomes, including bacteria, fungi, and archaea, play an unexpected yet critical role in helping plants survive salinity stress.
With nearly 10% of the world's land affected by high salinity, the impact on crop yield is devastating, with agricultural productivity in saline soils plummeting. Conventional methods to combat this stress have yielded limited success, and new strategies are urgently needed. The disruption of microbial communities in saline soils further complicates matters, as these microorganisms are essential for maintaining soil fertility and plant health. Given the growing concern over salinity's impact on food security, there is a pressing need for deeper exploration into how soil microbes can be used to support plant growth under these harsh conditions. This challenge highlights the necessity of understanding microbial ecosystems and their potential role in mitigating salinity stress.
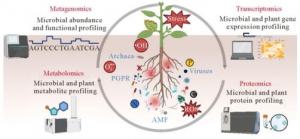
A recent study (DOI: 10.1016/j.pedsph.2024.09.002), published in Pedosphere in 2025, delves into the complex interplay between soil microorganisms and plants in salinity-affected environments. Led by a team from Kyungpook National University and the National Institute of Plant Genome Research, this research explores the potential of microbes such as plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB), archaea, and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in enhancing plant resilience to salinity. The study offers promising insights into how these microbes could be integrated into sustainable agricultural practices, providing a natural, eco-friendly way to protect crops from the growing threat of salinity.
The study reveals that under salinity stress, certain soil microbes thrive, forming crucial partnerships with plants. Among them, bacteria like Gammaproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes, along with fungi and archaea, help plants adapt by regulating water and nutrient uptake, enhancing antioxidant defenses, and producing growth-promoting phytohormones like indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). These microorganisms also help mitigate the harmful effects of salt by activating stress-tolerance genes, including those responsible for osmotic adjustment and ion transport. Interestingly, while salinity reduces the overall microbial diversity in soils, it favors salt-tolerant species that bolster soil fertility and plant health. This symbiotic relationship plays a pivotal role in sustaining both plant growth and soil ecosystem stability. The study underscores the importance of multiomics research to better understand these microbial interactions, offering new avenues for utilizing microbes to combat salinity stress and improve agricultural productivity.
"Salinity stress is one of the most pressing challenges for global agriculture today," said Dr. Jae-Ho Shin, lead author of the study. "Our research sheds light on the critical role that soil microbiomes play in alleviating this stress. By harnessing the power of these microorganisms, we can offer farmers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional solutions, enhancing crop resilience and productivity in saline-affected areas."
The implications of these findings are vast. By using plant growth-promoting microorganisms to enhance plant resilience, farmers could significantly reduce their dependence on chemical fertilizers and pesticides. The ability to restore soil health and promote sustainable farming practices in saline soils could revolutionize agriculture in regions affected by salinity. In the future, this research could lead to the development of microbial-based solutions tailored to specific crops and environments, offering a promising route for mitigating salinity stress and securing food production in a changing climate.
References
DOI
10.1016/j.pedsph.2024.09.002
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedsph.2024.09.002
Funding Information
This work was supported by the Biological Materials Specialized Graduate Program through the Korea Environmental Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI), funded by the Ministry of Environment of Korea, the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (No. PJ017033) through the Rural Development Administration of Korea, and the Regional Researcher Program (No. NRF-2020R1I1A307452212) through the National Research Foundation (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education of Korea. We also want to acknowledge the Korea Basic Science Institute (National Research Facilities and Equipment Center) Grant (No. 2021R1A6C101A416) funded by the Ministry of Education through the NGS Core Facility.
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Tower Crane Rental Market Size, Share, Competitive Landscape and Trend Analysis Report 2032
Donglify Launches Team Member Accounts: A Smarter Way to Share USB Dongles
Digital Manufacturing Market Analysis: Trends, Growth, and Future Outlook 2021-2030
Więcej ważnych informacji
 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

Konsument

Tylko 35 proc. Celów Zrównoważonego Rozwoju ONZ możliwe do osiągnięcia przed 2030 r. Potrzebna ściślejsza współpraca międzynarodowa
Jak wynika z raportu ONZ, choć w ciągu ostatniej dekady dzięki dążeniu do realizacji przyjętych celów udało się poprawić życie milionów ludzi na całym świecie, to jednak tempo zmian pozostaje zbyt wolne, by dało się je osiągnąć do 2030 roku. Postęp hamują przede wszystkim eskalacja konfliktów, zmiana klimatu, rosnące nierówności i niewystarczające finansowanie. Jak wynika ze sprawozdania Parlamentu Europejskiego, problemem jest także brak ścisłej współpracy międzynarodowej i sceptyczne podejście niektórych państw ONZ.
Przemysł spożywczy
UNICEF: Wszystkie dzieci poniżej piątego roku życia w Gazie cierpią z powodu niedożywienia. Sytuacja jest katastrofalna

Ataki Izraela na Strefę Gazy i jej izolacja doprowadziły do całkowitego załamania podstawowych usług i ograniczenia możliwości dostaw i dystrybucji pomocy humanitarnej – wskazuje UNICEF. W efekcie setki tysięcy Palestyńczyków są w sytuacji ciągłego zagrożenia życia i cierpią z powodu niedożywienia i głodu. Ta klęska dotyczy praktycznie wszystkich dzieci poniżej piątego roku życia. Konflikty są jednym z głównych przyczyn braku bezpieczeństwa żywnościowego, głodu i niedożywienia na świecie. Szczególnie dotyczy to Afryki i Azji Zachodniej.
Prawo
Branża ciepłownictwa czeka na unijną i krajową strategię transformacji. Liczy na większe fundusze i korzystne regulacje

Komisja Europejska zapowiedziała rozpoczęcie w I kwartale 2026 roku prac nad strategią dla ciepłownictwa i chłodnictwa. Nad tym strategicznym dokumentem w zakresie ciepłownictwa pracuje także polski rząd. Branża podkreśla, że obie te strategie będą miały kluczowe znaczenie dla trwającej transformacji w ciepłownictwie, czyli przyszłości ogromnych inwestycji, które czekają sektor do 2050 roku. Jednocześnie apeluje o większe wsparcie tego procesu ze środków publicznych.
Partner serwisu
Szkolenia

Akademia Newserii
Akademia Newserii to projekt, w ramach którego najlepsi polscy dziennikarze biznesowi, giełdowi oraz lifestylowi, a także szkoleniowcy z wieloletnim doświadczeniem dzielą się swoją wiedzą nt. pracy z mediami.

![Nestlé w Polsce podsumowuje wpływ na krajową gospodarkę. Firma wygenerowała 0,6 proc. polskiego PKB [DEPESZA]](https://www.newseria.pl/files/1097841585/fabryka-nesquik_1,w_85,r_png,_small.png)






.gif)

 |
| |
| |
|