MicroRNAs Offer New Hope in the Battle Against Adipose Tissue Fibrosis
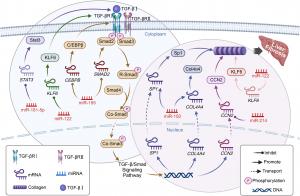
TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway and miRNA regulation in liver fibrosis. Tissue fibrosis intricately links with the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.
SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, April 20, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ --
A new review published in Genes & Diseases highlights the transformative role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in regulating and potentially reversing adipose tissue fibrosis, a condition closely linked to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Fibrosis, driven by abnormal extracellular matrix (ECM) accumulation, disrupts normal adipose tissue function and contributes to broader organ dysfunction. The review explores how miRNAs act as potent molecular regulators, capable of fine-tuning signaling pathways and gene expression patterns that influence fibrotic progression.
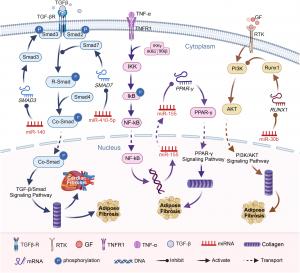
miRNAs, a class of small non-coding RNAs, can suppress or promote the translation of target genes involved in fibrogenic processes. Within adipose tissue, their regulation of pathways such as TGF-β/Smad, PI3K/AKT, and PPAR-γ plays a pivotal role in determining the balance between healthy tissue maintenance and pathological fibrosis. Specific miRNAs such as miR-122, miR-140, miR-150, miR-30b, and miR-155 demonstrate diverse functions, from blocking collagen synthesis to preventing the conversion of adipogenic cells into fibrogenic ones.
Of particular interest is the therapeutic application of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) transfected with targeted miRNAs. These engineered cells produce a secretome—a vesicle-rich fluid carrying anti-fibrotic miRNAs—that can be delivered to affected tissues without triggering immune rejection. This approach enables precise molecular intervention, targeting key proteins like Smad3, PDGFR-β, Runx1, and PPAR-γ, which are central to fibrosis development.
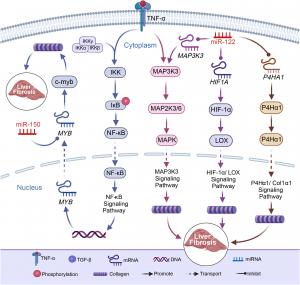
The review also draws attention to miRNAs’ systemic impact, noting how alterations in adipose tissue can influence fibrosis in distant organs, including the liver, heart, and kidneys. For example, miR-410-5p, elevated in high-fat diet-induced obesity, enhances fibrosis by downregulating protective factors like Smad7 in cardiac tissue. Conversely, restoring miR-140 or delivering miR-30b can mitigate these fibrotic responses.
Ultimately, the findings underscore the potential of miRNA-based therapies as a non-invasive, targeted strategy to combat fibrosis in both adipose tissue and other organs.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Mei Tian, Yang Zhou, Yitong Guo, Qing Xia, Zehua Wang, Xinying Zheng, Jinze Shen, Junping Guo, Shiwei Duan, Lijun Wang, MicroRNAs in adipose tissue fibrosis: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 4, 2025, 101287, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101287
Funding Information:
Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China LTGD24H070006
Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China LTGD23H150001
Medical and Health Research Project of Zhejiang Province, China 2023KY212
Medical and Health Research Project of Zhejiang Province, China 2024KY631
Zhejiang Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (China) 2024ZL249
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
editor|genesndiseases.com| |editor|genesndiseases.com
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Foundry512 Expands Talent Roster, Hiring for Key Roles Across Media, Accounts, Projects, and Creative
Turner Home Team Expands Home Buying Services Statewide: We Buy Houses Across North Carolina fast for cash.
Sullivan’s Castle Island and Castle Island Brewing Co. Launch 'Rickey Business' Lager to Celebrate James Beard Award
Kalendarium
Więcej ważnych informacji
 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

Prawo

KE proponuje nowy Fundusz Konkurencyjności. Ma pobudzić inwestycje w strategiczne dla Europy technologie
W środę 16 lipca Komisja Europejska przedstawiła projekt budżetu na lata 2028–2034. Jedna z propozycji zakłada utworzenie Europejskiego Funduszu Konkurencyjności o wartości ponad 400 mld euro, który ma pobudzić inwestycje w technologie strategiczne dla jednolitego rynku. Wśród wspieranych obszarów znalazła się obronność i przestrzeń kosmiczna. Na ten cel ma trafić ponad 130 mld euro, pięciokrotnie więcej niż do tej pory.
Firma
Były prezes PGE: OZE potrzebuje wsparcia magazynów energii. To temat traktowany po macoszemu

Choć udział odnawialnych źródeł energii w miksie energetycznym Polski jest stosunkowo wysoki i rośnie, to ten przyrost jest chaotyczny i nierównomiernie rozłożony miedzy technologiami – wskazuje Forum Energii. Dodatkowo OZE potrzebują wsparcia magazynów energii, a zdaniem Wojciecha Dąbrowskiego, prezesa Fundacji SET, ten temat jest traktowany po macoszemu. Brak magazynów powoduje, że produkcja energii z OZE jest tymczasowo wyłączana, co oznacza marnowanie potencjału tych źródeł.
Infrastruktura
Wzrost wynagrodzeń ekip budowlanych najmocniej wpływa na koszty budowy domu. Zainteresowanie inwestorów mimo to nieznacznie wzrasta

Budowa metra kwadratowego domu w Polsce kosztuje od 5,55 do 6 tys. zł w zależności od województwa – wynika z najnowszych analiz firmy Sekocenbud. Najdrożej jest w Warszawie, gdzie cena za metr kwadratowy domu przekroczyła już 6,2 tys. zł. Na przyrosty kosztów budowy domu wpływają zarówno drożejące materiały budowlane, jak i wyższe wynagrodzenia pracowników. Inwestorzy nie rezygnują jednak z budowy domów jednorodzinnych, co ma związek m.in. z wciąż wysokimi cenami mieszkań czy też obniżką stóp procentowych.
Partner serwisu
Szkolenia

Akademia Newserii
Akademia Newserii to projekt, w ramach którego najlepsi polscy dziennikarze biznesowi, giełdowi oraz lifestylowi, a także szkoleniowcy z wieloletnim doświadczeniem dzielą się swoją wiedzą nt. pracy z mediami.








.gif)

 |
| |
| |
|