Universal programming of 3D point spread functions for imaging
GA, UNITED STATES, July 10, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- UCLA researchers have introduced a framework for synthesizing arbitrary, spatially varying 3D point spread functions (PSFs) using diffractive processors. This approach enables unique imaging capabilities—such as snapshot 3D multispectral imaging—without relying on spectral filters, axial scanning, or digital reconstruction methods. The proposed framework could open up transformative possibilities for computational imaging, optical sensing and spectroscopy, as well as 3D optical information processing.
Engineers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering introduced a framework for universal point spread function (PSF) engineering, enabling the synthesis of arbitrary spatially varying 3D PSFs using diffractive optical processors. This development represents a significant step toward highly adaptable and programmable optical imaging systems.
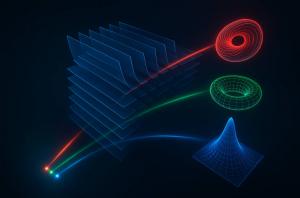
PSF engineering plays a significant role in modern microscopy, spectroscopy and computational imaging. Conventional techniques typically employ static phase masks at the pupil plane, which constrain the complexity and flexibility of the achievable PSF structures. The approach developed at UCLA enables arbitrary 3D PSF engineering through a series of passive surfaces optimized using deep learning algorithms, forming a physical diffractive optical processor.
Through rigorous numerical simulations, the researchers demonstrated that such diffractive processors can approximate arbitrary linear transformations between the 3D optical intensity distributions within the input and output volumes by synthesizing arbitrary 3D PSFs. This capability allows for precise control of light distribution in three dimensions, enabling sophisticated optical functions at the diffraction limit of light.
The framework would enable advanced imaging modalities, such as snapshot 3D multispectral imaging, achieved without the need for spectral filters, mechanical axial scanning, or digital reconstruction. These features are enabled through joint spatial and spectral PSF engineering, making the framework highly versatile.
This work marks a significant stepping-stone for future advances in computational imaging, optical sensing, and 3D optical information processing. Potential applications include compact multispectral imagers, high-throughput 3D microscopy platforms, and novel optical data encoding systems.
The study was conducted by Dr. Md Sadman Sakib Rahman and Dr. Aydogan Ozcan of the UCLA Electrical and Computer Engineering Department.
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-025-01887-x
Funding information
UCLA researchers acknowledge the funding of the US Army Research Office (ARO).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
Decorative Concrete Market Size, Trend, Growth, Competitive Insights, Leading Players by 2025-2032
Benzenoid Market Trends, Strategy, Application, Analysis, Global Share and Forecast-2031
Tom Jackobs Urges Entrepreneurs to Burn Their Old Sales Scripts This Fourth of July
Kalendarium
Więcej ważnych informacji
 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

 Jedynka Newserii
Jedynka Newserii

Prawo

KE proponuje nowy Fundusz Konkurencyjności. Ma pobudzić inwestycje w strategiczne dla Europy technologie
W środę 16 lipca Komisja Europejska przedstawiła projekt budżetu na lata 2028–2034. Jedna z propozycji zakłada utworzenie Europejskiego Funduszu Konkurencyjności o wartości ponad 400 mld euro, który ma pobudzić inwestycje w technologie strategiczne dla jednolitego rynku. Wśród wspieranych obszarów znalazła się obronność i przestrzeń kosmiczna. Na ten cel ma trafić ponad 130 mld euro, pięciokrotnie więcej niż do tej pory.
Firma
Były prezes PGE: OZE potrzebuje wsparcia magazynów energii. To temat traktowany po macoszemu

Choć udział odnawialnych źródeł energii w miksie energetycznym Polski jest stosunkowo wysoki i rośnie, to ten przyrost jest chaotyczny i nierównomiernie rozłożony miedzy technologiami – wskazuje Forum Energii. Dodatkowo OZE potrzebują wsparcia magazynów energii, a zdaniem Wojciecha Dąbrowskiego, prezesa Fundacji SET, ten temat jest traktowany po macoszemu. Brak magazynów powoduje, że produkcja energii z OZE jest tymczasowo wyłączana, co oznacza marnowanie potencjału tych źródeł.
Infrastruktura
Wzrost wynagrodzeń ekip budowlanych najmocniej wpływa na koszty budowy domu. Zainteresowanie inwestorów mimo to nieznacznie wzrasta

Budowa metra kwadratowego domu w Polsce kosztuje od 5,55 do 6 tys. zł w zależności od województwa – wynika z najnowszych analiz firmy Sekocenbud. Najdrożej jest w Warszawie, gdzie cena za metr kwadratowy domu przekroczyła już 6,2 tys. zł. Na przyrosty kosztów budowy domu wpływają zarówno drożejące materiały budowlane, jak i wyższe wynagrodzenia pracowników. Inwestorzy nie rezygnują jednak z budowy domów jednorodzinnych, co ma związek m.in. z wciąż wysokimi cenami mieszkań czy też obniżką stóp procentowych.
Partner serwisu
Szkolenia

Akademia Newserii
Akademia Newserii to projekt, w ramach którego najlepsi polscy dziennikarze biznesowi, giełdowi oraz lifestylowi, a także szkoleniowcy z wieloletnim doświadczeniem dzielą się swoją wiedzą nt. pracy z mediami.








.gif)

 |
| |
| |
|